Introduction
What is a patent?
A patent is a legal document that grants exclusive rights to an inventor for their invention. It provides the inventor with the right to prevent others from making, using, or selling their invention without their permission. Patents are granted by the government and are designed to encourage innovation by providing inventors with protection and incentives to develop and disclose their inventions. In order to obtain a patent, an inventor must meet certain criteria, including demonstrating that their invention is new, useful, and non-obvious. Once granted, a patent typically lasts for a limited period of time, during which the inventor can enforce their rights and potentially profit from their invention.
Importance of patents
Patents play a crucial role in today’s competitive business landscape. They provide inventors and companies with exclusive rights to their inventions, preventing others from using, selling, or profiting from their ideas without permission. This protection encourages innovation and promotes investment in research and development. Moreover, patents also serve as a valuable asset that can be licensed, sold, or used as collateral for securing funding. By granting inventors legal protection and financial incentives, patents foster a culture of creativity and entrepreneurship, driving economic growth and technological advancements.
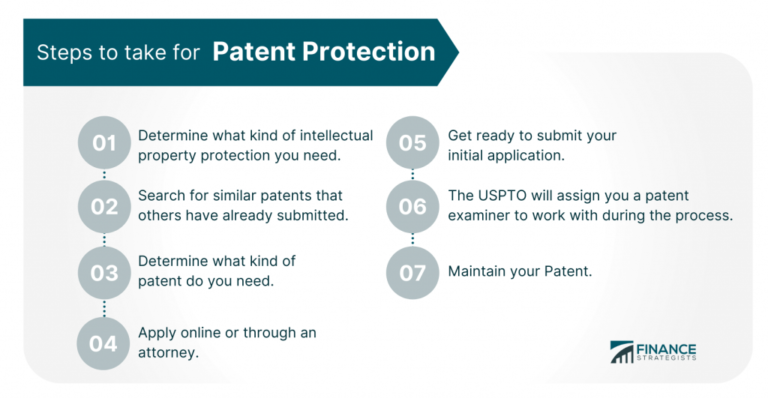
Overview of the patent process
The patent process is a complex and intricate journey that inventors and innovators must navigate in order to protect their intellectual property. It involves a series of steps and requirements that must be followed in order to obtain a patent. The process starts with the filing of a patent application, which includes a detailed description of the invention and its unique features. This is followed by a thorough examination by a patent examiner who evaluates the patentability of the invention. If the invention meets the criteria for patentability, it is granted a patent, providing the inventor with exclusive rights to the invention for a limited period of time. Throughout the process, it is important for inventors to consult with patent attorneys or agents who can guide them through the complexities of the patent system and ensure that their rights are protected.
Types of Patents

Utility patents
Utility patents are one of the most common types of patents granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). These patents are granted for new and useful processes, machines, articles of manufacture, or compositions of matter. Utility patents provide inventors with exclusive rights to their inventions, preventing others from making, using, or selling their creations without permission. To obtain a utility patent, inventors must demonstrate that their invention is novel, non-obvious, and has a practical application. The patent process for utility patents can be complex and time-consuming, requiring detailed documentation, patent searches, and examination by the USPTO. However, obtaining a utility patent can provide inventors with valuable protection for their inventions and the potential to profit from their innovative ideas.
Design patents
Design patents are a type of patent that protect the unique ornamental design of a functional item. Unlike utility patents, which protect the way an invention works or is used, design patents focus solely on the visual appearance of a product. This includes the shape, configuration, pattern, and surface ornamentation. Design patents are important for businesses and inventors who want to safeguard the aesthetic appeal of their products and prevent others from copying their designs. By obtaining a design patent, individuals and companies can establish exclusive rights to their unique designs and potentially gain a competitive edge in the market.
Plant patents
Plant patents are a specific type of patent that protect new varieties of plants. These patents are granted to individuals or companies who have invented or discovered a new and distinct variety of plant. In order to obtain a plant patent, the plant must be asexually reproduced, meaning it cannot be grown from seeds. Plant patents provide the patent holder with exclusive rights to the plant, including the right to sell, use, or reproduce the plant for a period of 20 years from the date of filing the patent application. This allows the patent holder to have a monopoly on the plant and its propagation, giving them a competitive advantage in the market.
Requirements for Patentability

Novelty
In the context of patent law, novelty refers to the requirement that an invention must be new and original. This means that the invention must not have been publicly disclosed or known before the filing date of the patent application. The novelty requirement is crucial in determining the patentability of an invention, as it ensures that only truly new and inventive ideas are granted patent protection. To meet the novelty requirement, an inventor must demonstrate that their invention has not been previously disclosed in any form, including in prior patents, scientific articles, or public demonstrations. The novelty of an invention is often assessed by conducting a thorough search of prior art, which includes all existing knowledge and technologies in the relevant field. If the invention is found to lack novelty, it will not be eligible for patent protection.
Usefulness
The usefulness of a patent is undeniable. It provides inventors with exclusive rights to their inventions, allowing them to protect their ideas and profit from their innovations. A patent ensures that inventors have the opportunity to fully develop and commercialize their inventions without fear of others copying or stealing their work. Furthermore, patents encourage innovation by incentivizing inventors to disclose their inventions to the public, thus contributing to the overall growth and advancement of society. In summary, patents play a crucial role in fostering creativity, promoting economic growth, and safeguarding intellectual property rights.
Non-obviousness
Non-obviousness is a crucial requirement in the patent process. It refers to the condition where an invention is not easily deducible or obvious to a person having ordinary skill in the relevant field. In other words, for an invention to be considered non-obvious, it must involve a significant leap or improvement over existing technology or knowledge. This requirement ensures that only truly innovative and groundbreaking inventions are granted patent protection. The determination of non-obviousness is subjective and often involves a careful examination of prior art and expert opinions. Patent examiners play a crucial role in assessing the non-obviousness of an invention and determining its eligibility for a patent. Overall, non-obviousness is a key criterion that ensures the patent system rewards and protects truly inventive and valuable inventions.
Patent Search

Why conduct a patent search?
Conducting a patent search is a crucial step in the patent process. It allows inventors and businesses to determine if their invention is unique and eligible for patent protection. By conducting a thorough search, individuals can identify existing patents and prior art that may affect the novelty and non-obviousness of their invention. This information is essential for making informed decisions about the potential success and viability of pursuing a patent. Additionally, a patent search can help inventors avoid potential infringement issues by identifying existing patents that their invention may infringe upon. Overall, conducting a patent search is an important first step in navigating the patent process and ensuring the protection and commercialization of innovative ideas.
How to conduct a patent search
Conducting a patent search is a crucial step in the patent process. It involves searching through existing patents and other relevant literature to determine if an invention is new and non-obvious. This search helps inventors and patent applicants understand the existing state of the art in their field and evaluate the potential patentability of their invention. By conducting a thorough patent search, inventors can identify prior art that may impact the patentability of their invention and make informed decisions on how to proceed with their patent application.
Tools for patent searching
When it comes to patent searching, there are several tools available that can help streamline the process. One popular tool is the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) website, which provides a comprehensive database of patents and patent applications. This website allows users to search for patents by various criteria, such as keyword, inventor name, or patent number. Another useful tool is Google Patents, which offers a user-friendly interface and access to a vast collection of patents from around the world. Additionally, there are commercial patent databases like Espacenet and WIPO’s PatentScope that provide advanced search options and additional features. These tools can greatly assist inventors, researchers, and patent professionals in navigating the patent process and conducting thorough patent searches.
Preparing a Patent Application

Components of a patent application
A patent application consists of several key components that must be included in order to successfully navigate the patent process. These components include a detailed description of the invention, drawings or diagrams illustrating the invention, claims that define the scope of protection sought, an abstract summarizing the invention, and any necessary supporting documentation. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the patent application, providing the necessary information for the patent examiner to assess the novelty, usefulness, and non-obviousness of the invention. By ensuring that all components are properly included and adequately described, applicants can increase their chances of obtaining a granted patent.
Writing the patent claims
Writing the patent claims is a crucial step in the patent process. Patent claims define the scope of protection that the inventor seeks for their invention. These claims should be clear, concise, and specific, outlining the unique features and aspects of the invention. It is important to carefully draft the claims to ensure that they are broad enough to cover potential variations of the invention, yet narrow enough to avoid being invalidated by prior art. Additionally, the claims should be supported by the detailed description and drawings included in the patent application. Writing the patent claims requires a thorough understanding of the invention and the ability to accurately and effectively communicate its novelty and inventiveness to the patent examiner.
Drafting the patent specification
Drafting the patent specification is a crucial step in the patent process. This is where the inventor describes the invention in detail, including its unique features and how it works. The patent specification must be clear, concise, and comprehensive, providing enough information for someone skilled in the field to understand and reproduce the invention. It is important to include all necessary technical details, diagrams, and examples to support the claims and ensure the patent is strong and defensible. A well-drafted patent specification increases the chances of obtaining a granted patent and protecting the inventor’s intellectual property rights.
Filing and Prosecuting a Patent

Filing the patent application
Filing the patent application is a crucial step in the patent process. It involves submitting a detailed description of the invention, along with any necessary drawings and supporting documents. The application must meet specific requirements set by the patent office, including clarity, novelty, and non-obviousness. Additionally, the applicant must pay the required fees and follow the prescribed filing procedures. Filing the patent application marks the official beginning of the patent process and sets the stage for examination and potential grant of the patent.
Patent examination process
The patent examination process is a crucial step in obtaining a patent. Once a patent application is filed, it undergoes a thorough examination by a patent examiner to determine its novelty, inventiveness, and industrial applicability. During this process, the examiner reviews the application to ensure it meets the requirements of patentability, such as being new, non-obvious, and useful. The examination process involves a detailed analysis of the application, including a search for prior art and a review of the claims made by the applicant. The examiner may also request additional information or amendments to the application to clarify or strengthen the claims. Overall, the patent examination process plays a vital role in ensuring that only deserving inventions are granted patent protection.
Responding to office actions
In the patent application process, after submitting your initial application, you may receive an office action from the patent office. An office action is a written communication from the patent examiner that outlines any issues or rejections with your application. It is essential to carefully review and understand the office action to effectively respond. When responding to office actions, it is important to address each issue raised by the examiner and provide clear and persuasive arguments or amendments to overcome any rejections. This process requires a thorough understanding of patent law and the ability to present your case convincingly. By responding thoughtfully and strategically to office actions, you can increase the chances of obtaining a successful patent for your invention.